Availability Calculations
Regulations require that government contractors determine availability of females and minorities by considering the following two factors:
- 41 CFR 60-2.14.c.1 The percentage of minorities or women with requisite skills in the reasonable recruitment area. The reasonable recruitment area is defined as the geographical area from which the contractor usually seeks or reasonably could seek workers to fill the positions in question.
- 41 CFR 60-2.14.c.2 The percentage of minorities or women among those promotable, transferable, and trainable within the contractor's organization. Trainable refers to those employees within the contractor's organization who could, with appropriate training that the contractor is reasonably able to provide, become promotable or transferable during the AAP year.
The Complete AAP software allows the user to consider more detailed factors within each of the two required factors:
- External
- • 1a: Local Census Area;
- • 1b: Non-local Census Area and
- • 1c: Training Institutions.
- Internal
- • 2a Promotable and Transferable; and
- • 2b Persons trainable
The Complete AAP software also allows users to use recruitment methods that are not covered by any of the other recruitment factors. This factor can be used to display available percentages of minorities and females in a pool of layoffs, an applicant flow pool, or another pool of the user’s choosing.
Contents
Calculations
Factor 1a
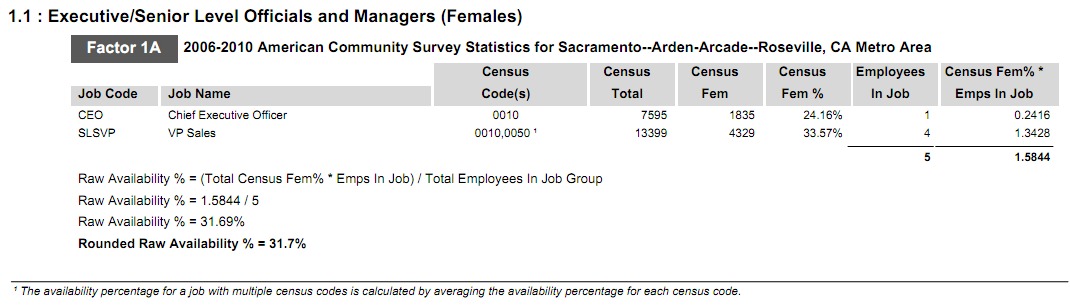
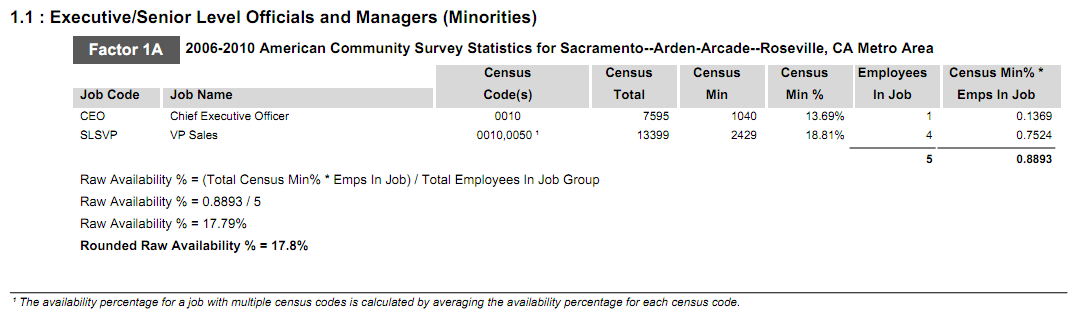
Factor 1a looks specifically at the census data in the local census area that the user assigns to each job group. This factor takes into consideration the specific census codes assigned to each job in every job group, and the number of minorities and females in the given census area who hold those jobs.
The total availability for females is calculated by adding the total number of employees in the contractor’s workforce who hold a job with a specific census code. That total is then multiplied by the percent of females available for that specific census code, and divided by the total number of employees in the job group. The totals are then summed to determine raw availability of females in the local census area. The total availability for minorities is calculated the same way using minority availability for the specific census code. This calculation is done for every census code in the job group. This method is illustrated below:
- Calculation of Factors
- Female Availability
- Minority Availability
Factor 1b
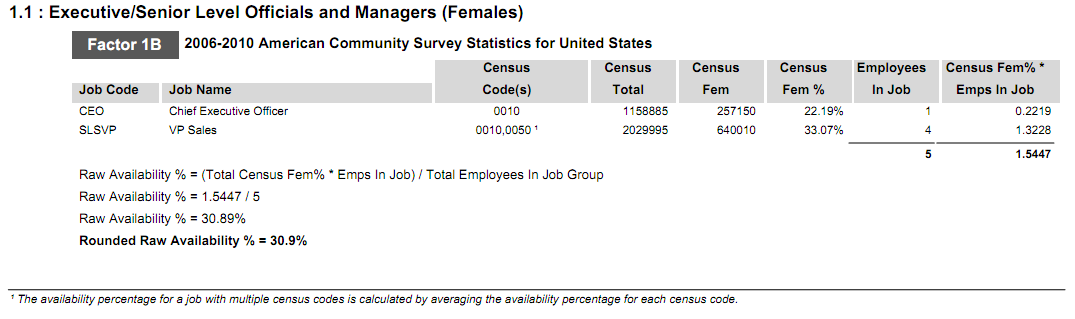
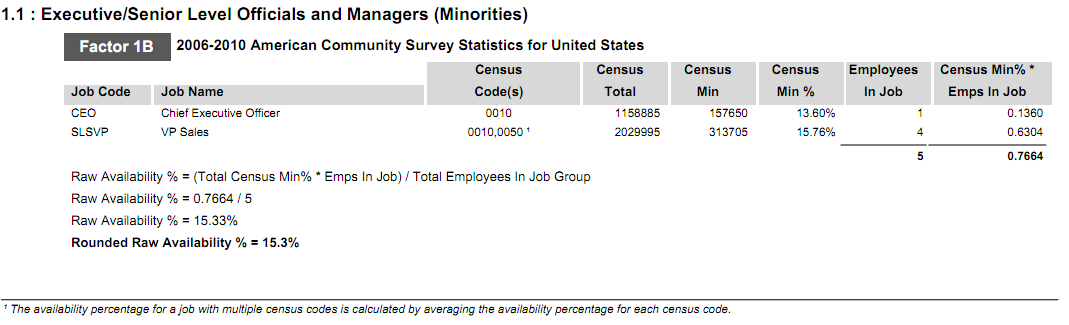
This factor looks specifically at the census data in the non-local census area that is assigned to each job group. This factor takes into consideration the specific census codes assigned to each job in every job group and the number of minorities and females in the given census area who hold those jobs.
The total availability for females is calculated by adding the total number of employees in the contractor’s workforce who hold a job with a specific census code. That total is then multiplied by the percent of females available for that specific census code, and divided by the total number of employees in the job group. The totals are then summed to determine raw availability of females in the local census area. The total availability for minorities is calculated the same way using minority availability for the specific census code. This calculation is done for every census code in the job group. This method is illustrated in the table using the following formulas:
- Calculation of Factors
- Female Availability
- Minority Availability
Factor 1c
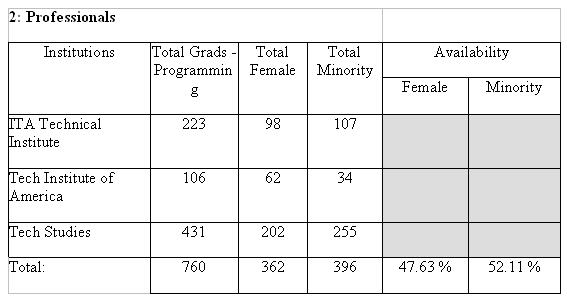
Factor 1c uses the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System’s (IPEDS) statistics to determine the availability of female and minority graduates in the institutions, disciplines, and awards sought by the employer.
Factor 2a
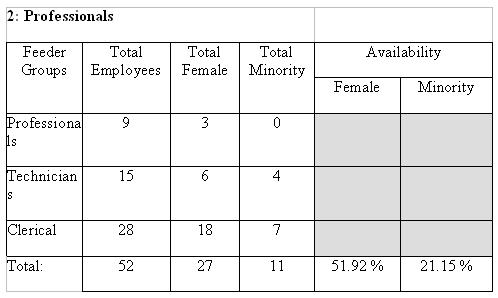
Factor 2a calculates the availability of promotable and transferable minorities and females within the feeder groups for each job group. The number of females in each feeder group is totaled. The total females in all feeder groups are added, and then divided by the number of employees in all feeder groups. Minority availability is calculated the same way. The table below illustrates the method used to determine availability for Factor 2a.
Factor 2b
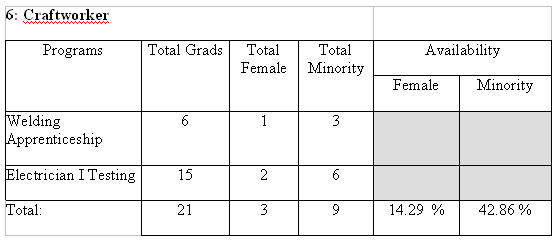
Factor 2b holds statistics of those employees within the contractor’s organization who could, with appropriate and formal training that the contractor is reasonably able to provide, become promotable or transferable during the AAP year. The type of training can range from apprenticeships to actual training courses, as long as they are formal, established programs. The training may involve a test that an employee must pass in order to complete the program. The total number of employees eligible for the program serves as the basis from which the availability of females and minorities is determined.
Factor 3
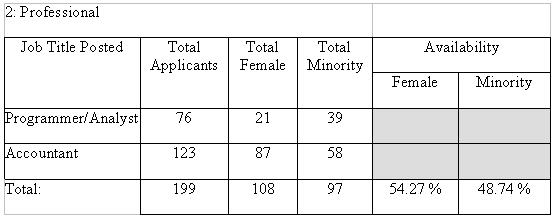
Factor 3 allows the user to utilize a customized factor. The availability for this factor is determined by the percent of females and minorities who are available using the factor chosen. An example of a custom factor that might be used is Applicant Flow. The same parameters should be followed for each job group that uses Factor 3.
See Also
Job Group Edit
Glossary for definitions of census area, feeder, and promotable
© Copyright Yocom & McKee, Inc.